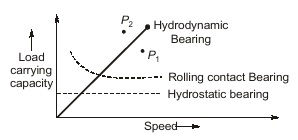
Comparison of Rolling and Sliding Contact Bearing
Hydrodynamic Bearing
- Higher starting friction (torque)
- Load carrying capacity vary directly with speed.
- It is suitable for shock, fatigue.
- It is used for high load, high speed application.
1. Hydro-static Bearing
- Load carrying capacity is independent of speed.
2. Rolling Contact Bearing
- Poor damping capacity.
- Requires low starting torque.
- Under full running capacity, friction loss is more as compared to hydrodynamic bearing.
- Suitable for frequent start/stop applications
- It requires more radial space [but hydrodynamic bearing requires more axial space]
- It is preferred for precise location of journal axis.
3. Heat Generated in a Bearing
Power Loss Due to Friction is Heat Generated
Ploss = μWV
Here, W = Radial load, V = Rubbing velocity
4. Heat Dissipation Equation
Hd = (Δt + 18)2 x A / K watt
Δt = Bearing temperature
A = l × d
K = 0.484 For unventilated bearing
= 0.273 For well-ventilated bearing
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Machine Design?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.