Crystal imperfections
Classification of Crystal imperfections
Crystal imperfections can be classified as:
- Point defects
- Interfacial defects
- Line defects
- Volume Imperfection
Types of Point Defects
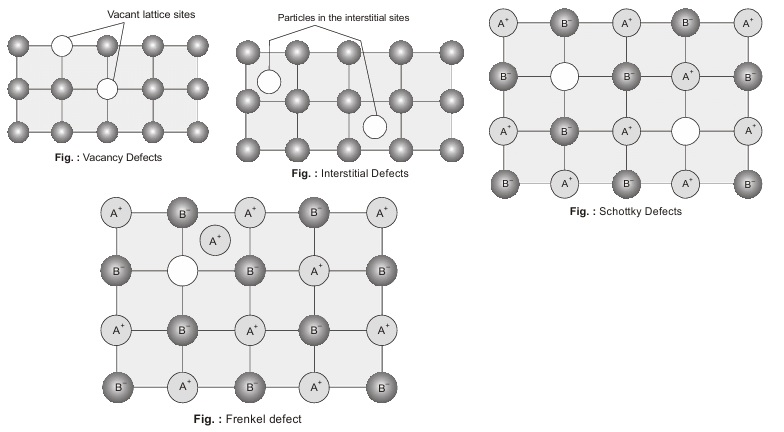
Vacancy Defects: When in crystalline substance, the points which were to be occupied by atom or an ion goes vacant i.e. lattice vacancy gets created then it is called vacancy defect. It is generally caused because of imperfect packing at time of crystallization or due to dislodging of atoms because of thermal vibrations. It results in decrease in density of the substance.
Interstitial Defects: When some extra constituents particles are present in the interstitial sites, the crystal is said to have interstitial defects. The defect results in the increase in the density of the substance.
Schottky Defects: In this there will always be cation-anion vacancy pair. In this a positively charged ion is removed thereby creating a vacancy, to counter balance this a negative ion is removed. Hence, neutrality is maintained. In the figure A+ and B– both are missing from lattice sites. As the number of ions decreases as a result of this defect, the mass decreases whereas the volume remains the same here, like vacancy defect density of solid decreases.
Frenkel Defect : If an ion or atom is missing from its lattice site (causing a vacancy or a hole there) and it occupies the interstitial site, electrical neutrality as well as the stoichiometry of composition are maintained, this type of defect is called Frenkel Defect.
Thus this defect is a combination of vacancy defect and interstitial defect.
Let,
nv = Number of vacancies in metal, nt = Total number of lattice sites in the metal
nv/nt = exp {E-kT}
nv/nt = Equilibrium concentration of vacancies, E = Enthalpy of formation of vacancy or Activation energy, k = Boltzmann constant, T = Absolute temperature
From above relation we can conclude that vacancy concentration in metal increases with increase in temperature.
Reason for formation of point defect :
- High energy particle radiation (i.e . thermal excitation)
- Excessive directional solidification.
Effect of formation of point defect :
- Vacancies decrease the strength of metal due to missing of few bonds.
- Impurities in metal result in lattice distortion due to size difference which develops randomly oriented planes between the neighbouring planes causing the slip to arrest and hence resistance to permanent deformation will increase, which decreases ductility and increases strength.
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

