Bolted Joint
Bolted Joint
- Threaded fastener designed to pass through holes in mating members and to be secured by tightening a nut from the end opposite to the head of the bolt.
- ANSI standard bolts and nuts of equal grades are designed to have the bolt fail before the threads in the nut are stripped.
Eccentric loading
There are many applications in which a bolted joint is subjected to eccentric loading. For example, wall bracket, pillar crane, etc.
Following are the different cases of eccentric loading:
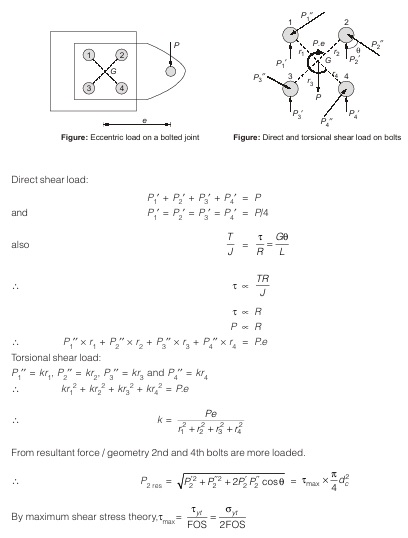
- Eccentric load in the plane containing the bolts.
- Eccentric load perpendicular to the axis of bolts.
- Eccentric load parallel to the axis of bolts.
Eccentric Load in Plane Containing the Bolts
- When an eccentric force is acting in the plane of bolts, it will produce two effects.
-
- Direct shear stress
- Shear due to moment set up at C.G.
- In this case, the line of action of the force does not pass through the C.G. of the bolt system.
- For the design of bolt subjected to eccentric load in the plane of bolt, following procedure is used:
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Machine Design?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

