Gusset Base
- Gusset base is provided where column load is too heavy or when the axial column load is accompanied by bending moments.
- It usually consists of two gusset plates, a base plate and two gusset angles when bolted connections are made. The gusset plates and the angles are placed on the column flanges as shown in figure below.
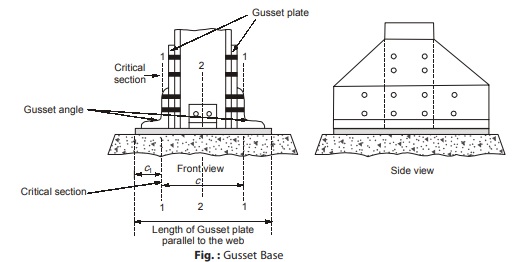
- Gusset plates increase the bearing area there by reducing the base plate thickness.
- Also, the gusset material supports the base plate against bending and thus results in smaller thickness of base plate.
- This type of base is considered as rigid.
- Where welded connections are used, there gusset angles are not required.
- The upward acting pressure from below the base causes bending of gusset plates thereby bringing the top edge of gusset in compression which may therefore buckle. This may be prevented by limiting the width to thickness ratio for the gusset plate.
Referring to figure below
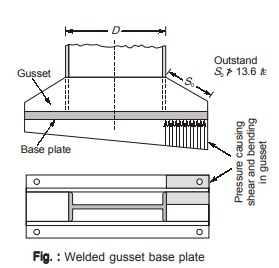
D ≤ 29.3 ε.tg for portion of gusset plate welded to the column flange
S0 ≤ 13.6ε.tg for the outstand of gusset plate from the edge of the column flange
Where tg = Thickness of gusset plate, ε √250 / fyg
- Gusset plates are designed to resist shear and bending. The moment in the gusset must not exceed the bending strength of the gusset plate.
- Bending strength of gusset plate is given by
Mdg = fyg / γm0 Ze
fyg = Design yield strength of gusset plate
Ze = Elastic section modulus of the gusset plate
γm0 = Partial safety factor = 1.1
- For columns provided with gusseted base, the gusset plates, gusset angles, stiffeners, fasteners, etc. in combination with the bearing area of the column should be sufficient to take the imposed and dead loads, bending moments and reactions to the base plate without exceeding the specified strength.
- In order to ensure a perfect contact, all the bearing surfaces must be machined.
- Where the column ends and gusset plates are not faced for complete bearing there the welding and fasteners connecting them to the base plate must be sufficient to transmit all the forces to which the base is subjected.

