Last Week Current Affairs: 12th MAR to 18th MAR 2025
Prepare for your competitive exam with the latest weekly current affairs from 12th March to 18th March, 2025, with MADE EASY! Whether you are appearing for UPSC CSE, ESE IRMS, SSC JE, RRB JE, or state-level exams, being informed is the key to success in exams. The MADE EASY Current Affairs article will help you get major news like PM Modi’s Mauritius visit, the Starlink satellite update, and the Chandrayaan-5 development in one place, which you can easily understand. Read this article completely now and start preparing for the exam.
Important events you should not miss for exam success
This week’s highlights are very important to prepare for the upcoming exam! From the World Air Quality Report 2024 to the Balochistan train hijack, from Mission Amrit Sarovar to the Astra missile milestone, these topics are crucial for your next exam. This article by MADE EASY analyzes all of these so that you are prepared for any question related to these that you may come across. Don’t wait—read this article today and be one step ahead in your exam preparation!
Boost your exam score with targeted current affairs insights.
Are you preparing for UPSC ESE, CSE, SSC JE, RRB JE, UPPSC AE, or any of the state-level exams and want to succeed in them? Knowledge is your strength, and we have you covered in detail in this article with updates on RBI’s Pravaah and Sarthi initiatives, SpaDeX Satellite, and much more. Our expert-prepared current affairs content is designed to help you succeed in these competitive exams. Read all the topics in detail below.
Weekly Current Affairs: 12th March to 18th March 2025
PM Modi’s Visit to Mauritius: 12 March 2024
Context: The Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid a state visit to Mauritius. He was the Chief Guest at Mauritius’ National Day Celebrations on March 12.
Key Highlights of the Visit
- MOUs Signed: Includes training civil servants, small and medium enterprises, blue economy development, combating financial crimes, and local currency settlement for trade.
- Indian Rupee Credit Line: A 487.6 crore INR line of credit for replacing water pipelines in Mauritius, a first-ever INR-based credit line.
- White-Shipping Agreement: Technical agreement for maritime security and information exchange.
- Award Conferred: PM Modi received the Grand Commander of the Order of the Star and Key of the Indian Ocean, marking him as the first Indian recipient.
- Vision for the Global South: PM introduced Vision MAHASAGAR (Mutual And Holistic Advancement for Security And Growth Across Regions), building on the previous Vision SAGAR.
About Mauritius
- Mauritius is a strategically located island nation in the western Indian Ocean, close to India.
- Nearly 70% of the population (1.2 million) of Mauritius is of Indian origin, strengthening ties with India.
- Mauritius was initially a French colony before becoming a British possession.
- Mauritius celebrates National Day on March 12, in honor of the date of Mahatma Gandhi’s Dandi March.
India- Mauritius Relations
- Diplomatic Relations: India and Mauritius established diplomatic relations in 1948 and have become key trading partners in the Asian continent.
- Commercial Relations: For the FY 2022-2023, Indian exports to Mauritius was USD 462.69 mn, Mauritian exports to India was USD 91.50 mn and Total trade was USD 554.19 mn.
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement: Signed in 1982 to help non-resident investors avoid double taxes.
- FDI Source: Mauritius is the second-largest source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India for FY 2023-24, after Singapore.
- Defence Relations: India is Mauritius’ preferred defence partner for acquiring platforms, capacity building, joint patrolling, hydrological services, etc.
- First Agreement: Transfer of a Dornier aircraft and an Advanced Light Helicopter (Dhruv) to Mauritius on lease.
- Second Agreement: A $100 million Line of Credit (LoC) for Mauritius to procure defence equipment.
- Space Cooperation: India and Mauritius are exploring space research opportunities and signed an MoU in November 2023 for developing a joint satellite.
- Development Partnership: India has been contributing to projects like the Metro Express, new hospitals, and infrastructure in Agaléga Island.
- SAGAR: The term SAGAR – ‘Security and Growth for All in the Region’ was coined by the PM in 2015 during his visit with a focus on the blue economy.
Starlink Satellite: 12 March 2024
Context: Elon Musk-owned SpaceX has secured agreements with Airtel and Jio to distribute Starlink, its satellite internet service.
About Satellite Internet
- Satellite internet is a wireless communication technology that provides broadband services using satellites orbiting the Earth. Unlike fiber-optic or mobile networks, which rely on ground infrastructure, satellite internet beams data from space-based satellites to user terminals on Earth.
- Types: Geostationary Orbit (GEO) Satellites (e.g., VSAT services)
- Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites (e.g., Starlink, OneWeb)
- Starlink is SpaceX’s satellite internet service that operates using a constellation of LEO satellites (over 7,000 satellites in orbit).
World Air Quality Report 2024: 12 March 2024
Context: According to the World Air Quality Report 2024, thirteen of the world’s top 20 most polluted cities are in India, with Byrnihat on the Assam-Meghalaya border being the most polluted.
Key Findings
- India is the fifth most polluted country in the world, with an average Air Quality Index (AQI) of 50.6 μg/m3 – 10 times higher than the World Health Organization’s (WHO) annual PM2.5 guideline value of 5 μg/m3.
- In 2023, India was the third most polluted country.

- Delhi continues to be the most polluted Capital city in the world with an average PM 2.5 concentration of 91.8 μg/m3.
- Out of the 138 countries and regions, 126 (91.3%) exceeded the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline value of 5 μg/m3. Only 17% of global cities met WHO air pollution guidelines.
- PM2.5 concentrations decreased in every country in Southeast Asia, though trans-boundary haze and lingering El Niño conditions remain major factors.
Balochistan Train Hijack: 13 March 2024
Context: The Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA) has claimed responsibility for hijacking the Jaffar Express.
About Balochistan
- It is the largest but least populated of Pakistan’s four provinces – Balochistan, Sindh, Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
- Ethnic Groups: Baloch, Brahui, and Pashtuns.
- It has substantial reserves of oil and gas, alongside gold and copper deposits, but has lagged in economic growth compared to other regions in the country.
- The province has been the site of a series of insurgencies, brutal state repression, and an enduring Baloch nationalist movement since 1948.
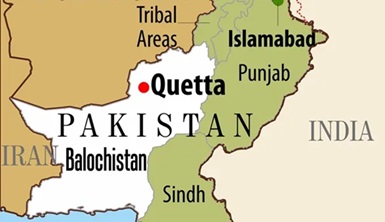
About Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA)
- The BLA are a Baloch ethnonationalist group who emerged in the 2000s with the aim of achieving independence for Balochistan.
- Pakistan banned the organisation in 2006, and the United States designated it as a global terrorist organisation in 2019.
India’s Stand on Balochistan
- Complex Position: India’s stance on Balochistan is shaped by geopolitics, regional stability, and its relationship with Pakistan. The India-Pakistan conflict over Kashmir makes any involvement in Balochistan a potential trigger for escalating tensions.
- Support for Self-Determination: India supports the right to self-determination for Balochistan’s people but avoids interfering in Pakistan’s internal affairs.
- Overall, India’s stance on Balochistan involves expressing concerns about human rights violations without interfering into the internal affairs.
Mission Amrit Sarovar: 13 March 2024
Context: The Indian Railways will dig ponds as part of the Union government’s Mission Amrit Sarovar that aims to address the critical issue of water scarcity in the country.
About Mission Amrit Sarovar
- It was launched on April 24, 2022, to conserve water for the future by developing and rejuvenating ponds (Amrit Sarovars) across India.
- It aims to develop or rejuvenate 75 Amrit Sarovars in each district of India, totaling approximately 50,000 pounds nationwide.
- Features:
- It is a “Whole of Government” approach with participation from multiple ministries:
- Rural Development, Jal Shakti, Culture, Panchayati Raj, Environment, Forest & Climate Change, and technical organizations.
- The works are being implemented by States and Districts with convergence from various ongoing schemes like:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), 15th Finance Commission Grants, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sichayi Yojna sub-schemes like Watershed Development Component and Har Khetko Pani.
- Public contributions such as crowdfunding and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) are allowed to support the initiative.
- Amrit Sarovars will provide opportunities for livelihood through activities such as irrigation, fisheries, duckery, water chestnut cultivation, water tourism, and other related activities.
- The ponds will act as social gathering points in the localities and serve as sites for flag hoisting on Independence Day.
- As of January 2025, over 68,000 Sarovars have been completed, improving surface and groundwater availability across various regions.
- Phase Two was launched with a focus on water availability, community participation (Jan Bhagidaari), strengthening climate resilience, and fostering ecological balance for lasting benefits.
Astra Missile: 13 March 2024
Context: The indigenously-built Tejas light combat aircraft successfully test-fired the Astra air-to-air missile off the coast of Chandipur, Odisha.
About
- Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Astra is an advanced beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) designed to engage targets over 100 km away.
- Equipped with advanced guidance and navigation systems, it ensures high precision in target engagement.
- Inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF), Astra strengthens India’s air defense with its ability to achieve speeds exceeding Mach 4 and reach a maximum altitude of 20 km, making it highly effective in air combat.
Pi (π) Day: 14 March 2024
Context: Every year on March 14, the world celebrates Pi Day, a tribute to the mathematical constant π (pi). The date (3/14) reflects the first three digits of pi i.e. 3.14.
About the Pi (π)
- Pi (π) is a mathematical constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter.
- It is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a finite fraction or a terminating decimal.
- Pi is approximately equal to 3.14159, but its decimal representation continues infinitely without repetition or pattern.
- Pi has been known since ancient times and plays a crucial role in fields like geometry, trigonometry, physics, and engineering.
Significance
- Mathematical Significance: Pi appears in formulas for circles, waves, and many natural phenomena.
- Promoting STEM Education: Pi Day serves as an opportunity to promote interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
- Historical Coincidence: Pi Day coincides with the birth anniversary of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879).
National Code Against Age Fraud in Sports 2025: 14 March 2024
Context: The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports in India has released the Draft National Code Against Age Fraud in Sports (NCAAFS) 2025.
Key Highlights
- This initiative aims to combat age fraud in sports, ensuring fair competition and protecting genuine athletes.
- The NCAAFS addresses age verification, penalties, and governance in sports.
- The NCAAFS seeks to implement a robust verification system through a centralised database.
- The code introduces strict penalties for those involved in falsifying age records. It also enhances transparency and accountability in sports governance, aligning with international best practices.
- All athletes must submit three mandatory documents during registration. Their age will be recorded in a secure digital database. This database will permanently lock the verified age to prevent future manipulation.
- In cases of age discrepancies, medical examinations will be conducted using the TW3 method, MRI scans, and general physical and dental assessments.
- The NCAAFS enforces strict penalties for age fraud violations. A first offence results in a two-year ban and forfeiture of titles. A second offence leads to a lifetime ban and legal action. Coaches and officials found guilty will also face penalties.
- A secure platform will allow stakeholders to report age fraud anonymously. A reward system will encourage whistle-blowers to come forward with genuine reports.
Bongosagar 2025: 15 March 2024
Context: The India-Bangladesh Naval Exercise Bongosagar 2025 recently took place in the Bay of Bengal.
Key Highlights
- This event marked step in strengthening the bilateral military relationship between India and Bangladesh.
- The exercise aimed to enhance maritime security through collaborative operations and interoperability between the two navies. INS Ranvir, a destroyer from the Indian Navy, and BNS Abu Ubaidah, a frigate from the Bangladesh Navy, were the main vessels involved.
- The primary goal of Bongosagar 2025 was to improve joint operational capabilities. This included enhancing coordination for maritime security challenges. The exercise aimed to facilitate seamless operations between the Indian Navy and the Bangladesh Navy.
- The exercise featured a diverse range of activities. These included surface firing exercises, tactical manoeuvres, and underway replenishment. Additional operations like Visit-Board-Search-Seizure (VBSS) drills and communication exercises were also conducted. These activities were designed to test and improve the operational readiness of both navies.
Significance
- Bongosagar 2025 played important role in encouraging closer ties between India and Bangladesh. The exercise aimed to build trust and confidence in joint operations. This collaboration is vital for addressing regional security concerns.
- The exercise contributes to the broader Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative. This initiative promotes stability and security in the Indian Ocean region. By enhancing naval cooperation, both countries aim to counter global security challenges effectively.
Chagos Archipelago: 15 March 2024
Context: The Chagos Archipelago, located in the Indian Ocean, has been a focal point of territorial disputes between Mauritius and the United Kingdom.
Key Facts
- The islands in Chagos Archipelago were under British control for decades after Mauritius gained independence in 1968.
- Recent developments have seen the UK formally acknowledge Mauritius’ claims over the archipelago, but tensions remain, particularly regarding Diego Garcia, which hosts USA military base.
- The US established a military base on Diego Garcia in the 1970s. The base became operational in 1986 and has since played important role in US military operations in the region.
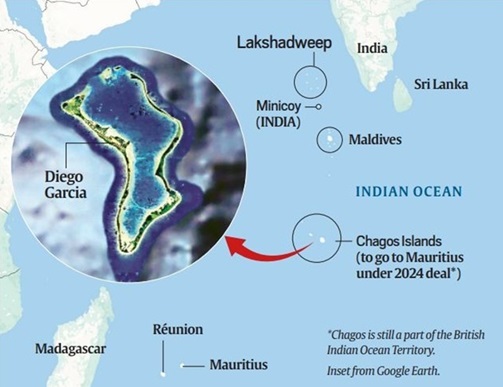
Historical Background
- The Chagos Archipelago comprises over 60 islands, with Diego Garcia being the largest.
- Initially uninhabited, Chagos saw its first permanent settlements in the 18th century.
- The French claimed the islands in the 1700s, and later, British control was established after the Napoleonic Wars. The islands were used for plantations, relying on slave and indentured labour.
About British Indian Ocean Territory
- In 1965, the UK created the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which included Chagos. This move was part of a broader strategy to maintain military presence in the Indian Ocean during the Cold War.
- In 2017, the UN General Assembly requested the International Court of Justice (ICJ) to assess the legal status of the islands. The ICJ ruled in 2019 that the UK must end its administration over Chagos. The UN subsequently called for the UK to withdraw from the area.
Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201 Microprocessors: 16 March 2024
Context: Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced the development of two advanced 32-bit microprocessors, Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201.
Key Facts
- Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201 processors are designed for space applications and represent leap in India’s indigenous technology capabilities. They were developed in collaboration with the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL) in Chandigarh.
- Vikram 3201 is India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit microprocessor. It is designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space. The processor supports floating-point computations and offers high-level language compatibility, particularly with Ada. The in-house development of software tools further enhances its functionality.
- Vikram 3201 was validated in the Mission Management Computer during the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM-4) mission. This successful validation puts stress on its reliability for future space missions.
- Kalpana 3201 is based on the SPARC V8 architecture. It is a Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) microprocessor, compatible with open-source software. This design facilitates integration with various software development tools, making it versatile for different applications.
Supersolid Light: 16 March 2024
Context: Recent advancements in quantum physics have revealed a remarkable phenomenon – light can be transformed into a “supersolid.”
Key Facts
- This breakthrough, achieved by Italian researchers, marks a new phase of matter that combines the properties of solids and superfluids.
- The implications of this discovery extend to various fields, including quantum computing and materials science.
About Supersolid Light
- A supersolid is an exotic state of matter that exhibits both solid-like rigidity and the ability to flow without friction.
- Previously, this state was only observed in Bose-Einstein condensates, which require extreme cooling. The recent research demonstrates that light can also achieve this state, altering our understanding of light and matter.
- Researchers employed innovative quantum techniques to create a supersolid state in light. They used a semiconductor platform to manipulate photons similar to electron behaviour in conductors. By firing a laser into a gallium arsenide structure with microscopic ridges, they produced hybrid light-matter particles called polaritons. As photon density increased, satellite condensates formed, indicating supersolid behaviour.
- The discovery of supersolid light holds immense potential for quantum technology. It could enhance the stability of quantum bits (qubits), crucial for quantum computing advancements. Additionally, the ability to manipulate light in this manner may revolutionise optical devices and photonic circuits, paving the way for breakthroughs in fundamental quantum mechanics research.
Chandrayaan-5 Mission: 17 March 2024
Context: The Indian government has approved the Chandrayaan-5 mission to study the Moon.
Chandrayaan Missions
- Chandrayaan-1 (2008): Made chemical, mineralogical, and photo-geological maps of the Moon in
- Chandrayaan-2 (2019): Its lander crashed, but the orbiter sent hundreds of images of the Moon’s surface.
- Chandrayaan-3 (2023): It was a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2, to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. It was able to have the Vikram lander successfully soft-land on the moon’s south pole region on August 23, 2023.
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission: It is expected to be launched in 2027. It will aim to collect samples of the lunar soil from the moon and bring the back to the earth for further study.
- Chandrayaan-5 Collaboration with Japan: The mission will be conducted in association with Japan. Unlike the Chandrayaan-3 mission, which carried a 25-kg rover, Chandrayaan-5 will carry a 250-kg rover to study the Moon’s surface.
Five Eyes Intelligence Alliance: 17 March 2024
Context: The Five Eyes intelligence alliance is facing challenges due to shifts in U.S. foreign policy during the Presidency of Donald Trump.
About Five Eyes Intelligence Alliance
- It is one of the most powerful and secretive intelligence-sharing alliances in the world, comprising the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
- Origins and Evolution:
- The foundation of Five Eyes was laid during the Second World War when the US and UK signed the UKUSA Agreement in 1946, formalizing their intelligence-sharing mechanism.
- Canada (1948), Australia (1956), and New Zealand (1956) later joined, creating a trusted circle of Anglo-Saxon nations dedicated to seamless intelligence collaboration.
- Initially focused on monitoring Soviet communications during the Cold War, the alliance adapted over time to cover terrorism, cyber warfare, and threats from rising global powers.
- It operates primarily through agencies such as:
- United States: National Security Agency (NSA)
- United Kingdom: Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ)
- Canada: Communications Security Establishment (CSE)
- Australia: Australian Signals Directorate (ASD)
- New Zealand: Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB)
- It uses advanced surveillance tools such as the ECHELON system, a vast global interception network capable of monitoring communications across various platforms, including emails, phone calls, and online activities.
RBI’s Pravaah and Sarthi Initiatives: 17 March 2024
Context: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been awarded the Digital Transformation Award 2025 for Digital Initiatives by Central Banking, London.
Digital Initiatives By RBI
- The award highlights the RBI’s commitment to innovation and efficiency in governance through its groundbreaking digital initiatives, Pravaah and Sarthi.
- Sarthi System:
- It is an internal workflow digitization system that has streamlined record management, automated processes, and enhanced data analysis.
- It has eliminated the reliance on manual paperwork, boosting operational efficiency across RBI departments by enabling secure digital submissions and improving collaboration.
- Pravaah System:
- It serves as a digital regulatory application platform for external users. It allows seamless submission and processing of regulatory applications, integrating directly with the Sarthi database.
- It has significantly reduced paperwork, enhanced transparency, and improved cybersecurity in financial documentation.
SpaDeX Satellites: 18 March 2024
Context: Nearly two months after ISRO successfully docked two satellites in space, it carried out an undocking procedure recently.
Key Highlights
- This makes India the fourth country after the US, Russia, and China to demonstrate space docking and undocking capabilities.
- To demonstrate this capability, ISRO launched the experimental SpaDex mission on December 30, 2024.
About Space Docking
- Space docking is the process of bringing two fast-moving spacecraft into the same orbit, gradually bringing them closer, and physically joining them together.
- This is a highly complex maneuver requiring precise navigation, automated control, and real-time adjustments.
- Benefits:
- Enabling Heavy Space Missions:Large spacecraft cannot be launched in one go due to weight limitations.
- Docking allows modular spacecraft assembly in orbit, similar to the International Space Station (ISS).
- Critical for Future Human Spaceflight:Essential for transporting astronauts & supplies to India’s planned space station by 2035.
- Key to India’s crewed lunar missions (by 2040) under Gaganyaan & future Moon missions.
- Supports Lunar Sample Return Missions: Chandrayaan-4, India’s future mission to bring back lunar soil and rock samples, will rely on docking technology.
- Advancing In-Space Servicing & Robotics: Enables repairing, upgrading, and refueling satellites in orbit without launching new ones.
About India’s Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX)
- Objective: To demonstrate in-space docking, rendezvous, and undocking capabilities.
- Satellites Used:
- SDX01 (Chaser Satellite): Actively approached and docked with the target.
- SDX02 (Target Satellite): Served as the docking module.
- Launch Vehicle: PSLV-C60
- Orbit: 470 km circular orbit
- Developed by: UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), Bengaluru, with support from other ISRO centers.
National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA): 18 March 2024
Context: The National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA) aims to create a comprehensive national database, ensuring the preservation of India’s rich cultural legacy.
Key Facts
- India is one of the largest repositories of tangible heritage, with monuments, sites, and antiquities spanning from prehistoric times to the colonial era.
- While various organizations like the ASI, State Archaeology Departments, and INTACH have documented parts of this heritage, much remains scattered or undocumented. The absence of a unified database makes research, conservation, and management challenging.
National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA)
- Established in 2007, the NMMA is responsible for the digitization and documentation of India’s built heritage and antiquities.
- Budget Allocation: Rs. 20 lakh were allocated for NMMA in the FY 2024-25.
- Objectives: Documenting and creating a national database of built heritage, monuments, and antiquities for better management and research.
- Enhancing collaboration between the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), state departments, and other stakeholders.
To read all the current affairs of the last year, click on the link below:
🔗Download the Complete Current Affairs PDF for Free Now!
Must Read: 🔗 26th FEB to 4th MAR 2025 Weekly Current Affairs
MADE EASY Offline and Online Courses
| MADE EASY Classroom & Live-Online Courses: Enroll Now 👇 | |
|---|---|
Classroom Courses |
|
| GATE | GATE+ESE |
| GATE+SES | GATE+ESE+SES |
| Conventional Course | Offline Test Series |
| G.S. & Engg. Aptitude Batch | Interview Guidance |
Live-Online Courses |
|
| GATE+SES | GATE+ESE |
| GATE+ESE+SES | JE & AE |
| Rank Improvement Course | RRB-JE |
| UPPSC-AE | State Exams (GS) Course |
Are you looking for Current Affairs 2024?
If yes then buy the book given below today and strengthen your exam preparation.
- Book Name: Current Affairs Quarterly Issue: July-August-September 2024
- Publisher Name: MADE EASY Publications
- MRP: ₹ 200.00
- Price: ₹ 170.00 (15% OFF)
🔗 Buy Now | 🔗 Explore and Buy Other Books
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.






