Types of Vibration
- Free Vibrations: Elastic vibrations in which there are no friction and external forces after the initial release of the body.
- Forced Vibrations: When a repeated force continuously acts on a system, the vibrations are said to be forced vibration. The frequency of the vibrations is that of the applied force and is independent of their own natural frequency of vibrations.
- Damped Vibrations: When the energy of a vibrating system is gradually dissipated by friction and other resistances.
- Un-damped Vibrations (Hypothetical): When there is no friction or resistance present in system to contract vibration.
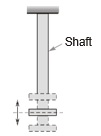
- Longitudinal Vibrations: If the shaft is elongated and shortened so that the same moves up and down resulting in tensile and compressive stresses in the shaft.
- Harmonic vibration: Vibration in which the motion is a sinsuoidal function of time.
- Fundamental vibration: Harmonic component of a vibration with the lowest frequency.
- Steady state vibration: When the particles of the body move in steady state condition or continuing period vibration.
- Transient vibration: Vibratory motion of a system other than the steady state.
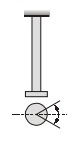
- Transverse Vibrations: When the shaft is bent alternately and tensile and compressive stresses due to bending result.
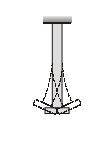
- Torsional Vibrations : When the shaft is twisted and untwisted alternately and torsional shear stresses are induced.
Free Longitudinal Vibrations
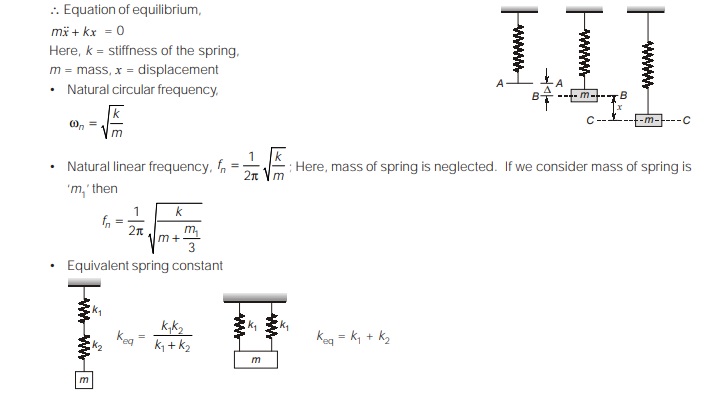
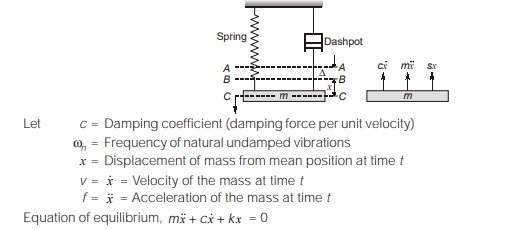
Damped Longitudinal Vibration
Dunkerley’s Method
Let W1, W2, W3, … be the concentrated loads on the shaft due to masses m1, m2, m3, … and δ1, δ2, δ3 … the static deflections of this shaft under each load when that load acts alone on the shaft. Let the shaft carry a uniformly distributed mass of m per unit length over its whole span and the static deflection at mid-span due to the load of this mass be δs. Also, let
fn = Frequency of transverse vibration of the whole system

<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is the Theory of Machines?
WhatsApp Group
Join Now
Telegram Group
Join Now


