What is Power Electronics?
Power electronics combine power, electronics, and control. Control deals with the steady-state and dynamic characteristics of a closed-loop system. Power deals with static and rotating power equipment for the generation, transmission, and distribution of electric energy. Electronics deal with the solid state devices and grants for signal processing to meet the desired control objectives.
Power electronics may be defined as the application of solid- state electronics for the control and conversion of electric power. One could also define power electronics as the art of converting electrical energy from one form to another in an efficient, clean, compact, and robust manner for the energy utilization to meet the desired needs.
Here are some links to important topics that will help you understand power electronics better if you want to study more about it:
Key Concepts:
The inter-relationship of power electronics with power, electronics, and control is shown in the below figure.
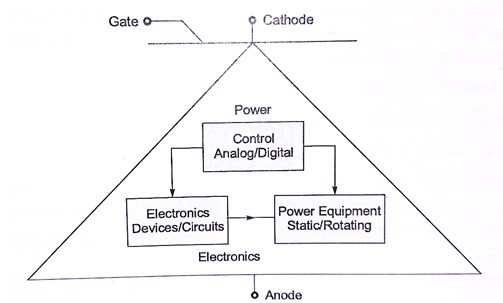
By looking at the figure, the arrow points to the direction of the current flow from anode (A) to cathode (K). It can be turned on and off by a signal to the gate terminal (G). Without any gate signal, it normally remains in the off state, behaves as an open circuit, and can withstand a voltage across the terminal A and K.The task of power electronics is to process and control the flow of electric energy by supplying voltages and currents in a form that is optimally suited for user loads.
History of Power Electronics
The history of power electronics began with the introduction of the mercury arc rectifier in 1990. The first electronics revolution began in 1948 with the invention of the silicon transistor at Bell Telephone Laboratories by Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley. The next breakthrough, in 1956, was also from Bell Laboratories: the invention of the PNPN triggering transistor, which was defined as a thyristor or silicon controlled rectifier (SCR). The second electronics revolution began in 1958 with the development of the commercial thyristor by the General Electric Company. That was the beginning of a new era of power electronics. The microelectronics revolution gave us the ability to process a huge amount of information at incredible speed. The power electronics revolution is giving us the ability to process a huge amount of information at incredible speed. The power electronics revolution is giving us the ability to shape and control large amounts of power with ever increasing efficiency.
Scope of Power Electronics
Power Electronics is one of the important topics in electrical engineering which have lots of scope:
- Renewable energy
- Electric transportation
- Consumer electronics
- Industrial Automation
- Power distribution and transmission
- Defense and aerospace
A power electronic engineer can also work in academics, research, and in new developing technologies. To pursue a career as a power electronics engineer, one must have a bachelor’s or master’s degree in electrical engineering.
Online Courses for Power Electronics:
A bachelor’s or master’s degree is very important to pursue a successful career in electrical engineering. But a strong grasp on key topics and subjects is equally important. Particularly, students preparing for government engineering exams may encounter intense competition. So MADE EASY Courses and the experts are here to provide guidance and support during your preparation journey for GATE, ESE, RRB JE and PSU exams. The courses focus on providing quality lectures from the basic level to the advanced level. MADE EASY provides aspirants with the right guidance to maximize their performance and achieve success. Electrical engineering candidates are advised to visit the links given below to learn more about courses that include key concepts of engineering branches taught at the basic level and prepare aspirants for the future.
- GATE : 1 Year Foundation Course
- ESE+GATE : 1 Year Foundation Course
- GATE + SES (GS) : 1 Year Foundation Course
- GATE & SES (GS) 2026-27 Live Online Foundation Course
- ESE + GATE + SES (GS) 2026-27 Live Online Foundation Courses
Recommended Books for Power Electronics
Books are still an essential part of learning as they offer in-depth knowledge in various topics. Learning books are well structured and provide comprehensive understanding making them invaluable for students and lifelong learners. MADE EASY Publications is one such platform for students who are looking for high quality and well structured content for their preparation. Our platform consists of government engineering exams books which are curated by a team of experts and experienced authors. Electrical engineering aspirants are suggested to click on the links mentioned below to learn more in depth about power electronics:
- GATE-2026: Electrical Engineering Previous Year Solved Papers
- ESE 2026: Preliminary Exam: Electrical Engineering Objective Solved Paper Vol-1
- A Handbook on Electrical Engineering
FAQs:
1. How many types of power electronics circuits are there?
Ans. Power electronics circuits include: Diode Rectifiers, AC to DC Converters (Phase- controlled rectifiers), DC to DC Converters (DC Choppers), DC to AC Converters (Inverters), AC to AC Converters, and Static Switches.
2. What is a silicon controlled rectifier?
Ans. A silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) is a solid-state device that controls the flow of current in one direction
3. What is SCR and how does it work?
Ans. Silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs), also known as thyristors, are solid state devices that control the flow of current in circuits.
4. What is a MOSFET and why is it used?
Ans. A metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is a three-terminal semiconductor device that’s used to switch or amplify electrical signals.
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.