PANTOGRAPH
A pantograph is a four-bar linkage used to produce paths exactly similar to the ones traced out by a point on the linkage. The paths so produced are, usually, on an enlarged or reduced scale and may be straight or curved ones.
Pantograph is a geometrical instrument used in drawing offices for reproducing given geometrical figures or plane areas of any shape, on an enlarged or reduced scale. It is also used for guiding cutting tools. Its mechanism is utilized as an indicator rig for reproducing the displacement of cross-head of a reciprocating engine, which, in effect gives the position of displacement.
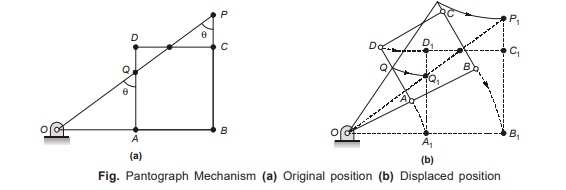
Fig. (a) shows the line diagram of a pantograph in which AB = CD, BC = AD and ABCD is located/jointed in such a way that it remains in a parallelogram position. OQP is a straight line and P describes a path similar to that described by Q.
Proof : To prove that the path described by P is similar to that described by Q, let us consider similar triangles ΔOAQ and ΔOBP in which ∠BOP is common.
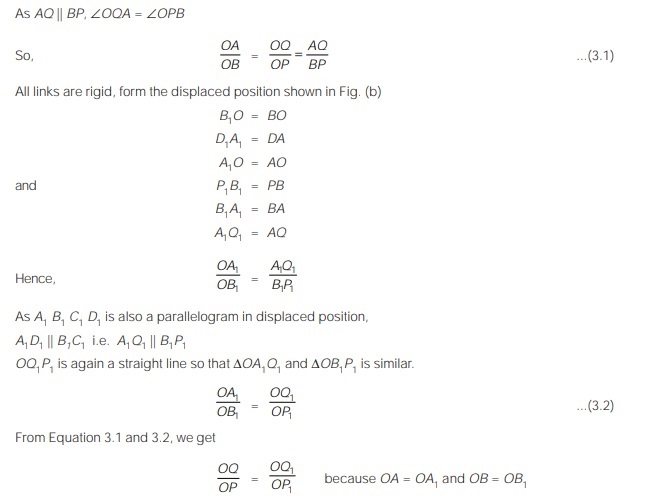
Hence, OQ1 is similar to OP1 or they are parallel. Thus, path traced by P is similar to that of Q.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is the Theory of Machines?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

