Four-Bar Mechanism
Grashof’s law
s + l ≤ p + q 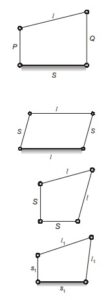
Here, s = Shortest link, l = Longest link
p, q = Remaining links
Case-I
If s + l < p + q
– s is fixed – Double crank mechanism.
– p or q fixed – Crank-rocker mechanism
– l is fixed – Rocker-rocker mechanism
Case-II
If s + l = p + q
– All link have different lengths then same as case-I.
– Parallelogram linkage-crank-crank mechanism.
i.e. s = p, l = q
– s is fixed – Double crank mechanism.
– l is fixed – Double crank mechanism.
– Deltoid linkage
- s is fixed – Crank-crank mechanism.
Also called as kite mechanism. - l is fixed – Crank-rocker mechanism.
Case-III
s + l > p + q (Grashof’s law is not satisfied and it will give rocker-rocker mechanism.)
Inversions of Slider-Crank Mechanism
- First Inversion-link 1 is fixed: Reciprocating engine/compressor.
- Second Inversion-link 2 is fixed (Crank): Whitworth quick return
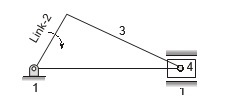 mechanism, rotary (radial) engine.
mechanism, rotary (radial) engine. - Third Inversion-link 3 is fixed (Connecting rod): Crank and slotted lever mechanism, oscillating cylinder mechanism.
- Fourth Inversion-link 4 is fixed (Slider): Hand pump, bull engine.
Mechanical Advantage

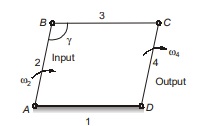
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is the Theory of Machines?

