What is the effect of clearance volume on compressor?
- Clearance volume is represented as a percentage of stroke volume.
- High pressure air left in clearance volume expand at the end of delivery stroke and suction for the second cycle starts only when the air pressure falls to the atmospheric pressure.
- If compression and expansion follow the same polytropic law then the workdone per cycle will be given by the area 12-3-4-1 on p –V diagram.
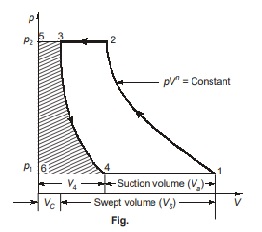
W (area 1-2-3-4-1) = Wcomp (area 1-2-5-6-1) – W exp(area 3-4-5-6)
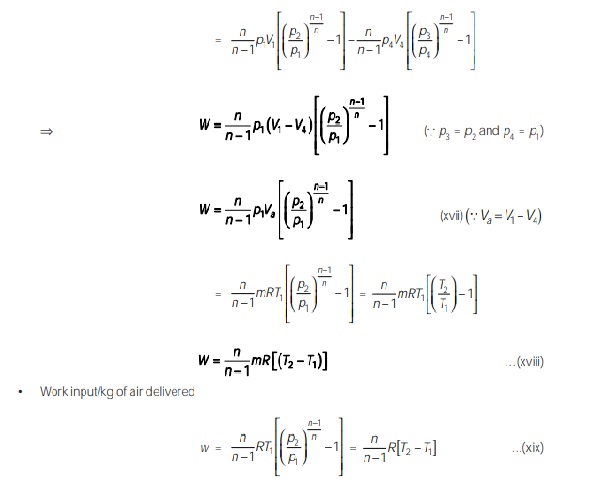
- Clearance volume does not affect the work of compression per kg of air. [Refer equation (xvi) and (xix)].
- Free air delivered per cycle
FAD = Va = (V1 – V4) = Effective swept volume - FAD (free air delivered-m3/min) is the actual volume delivered at intake temperature and pressure.
Displacement is the actual volume (m3/min) swept out per min. by piston during suction stroke.
FAD < Swept Volume due to the Following Reasons
- Clearance space is filled with high pressure air, which expand to a pressure below the atmospheric pressure than only the suction valve will automatically open: therefore a portion of suction stroke is wasted.
- Due to hot cylinders, air entering into the cylinder expands and thus reduce the FAD.
- Fluid resistance through the air intake, valves etc. prevents the cylinder being fully charged with air at atmospheric conditions.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Power Plant Engineering?
WhatsApp Group
Join Now
Telegram Group
Join Now

