What is Rotary Compressors and Its Types?
Rotary compressors are used to supply continuous pulsation free compressed air. They have rotors and casing in place of piston cylinder arrangement. Rotary compressors are compact well balanced, and high speed compressors. Due to low starting torque they can be directly coupled with prime-mover. They handle large mass of gas and are suitable for low and medium pressure ratios.
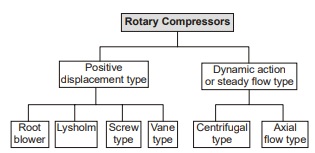
- Rotary compressors are the steady flow compressors and examples are centrifugal compressor and axial flow compressor.
- In steady flow compressor ➡️ Compression occurs by transfer of KE from the rotor.
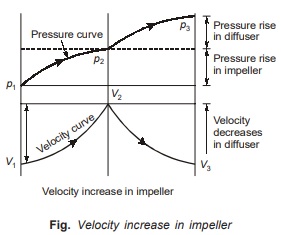
Working of Centrifugal Compressor
- Air enters the eye of impeller with low velocity V1 and atmospheric pressure p1.
Impeller transfers the energy of drive to the air, due to which static pressure, temperature and velocity increases. Let the increased pressure and velocity be p2 and V2 respectively.
Work input in impeller = Rise in total temperature
- Now air enters into diffuser (diverging section) where velocity decreases to V3.
K.E. is converted into pressure energy which causes further rise in static pressure p3 as shown in figure.
- Pressure energy achieved in impeller = Pressure energy achieved in diffuser
With single-stage centrifugal compressor, pressure ratio of 5 : 1 can be achieved
And with multi-stage centrifugal compressor, a pressure ratio of 12 : 1 can be attained.
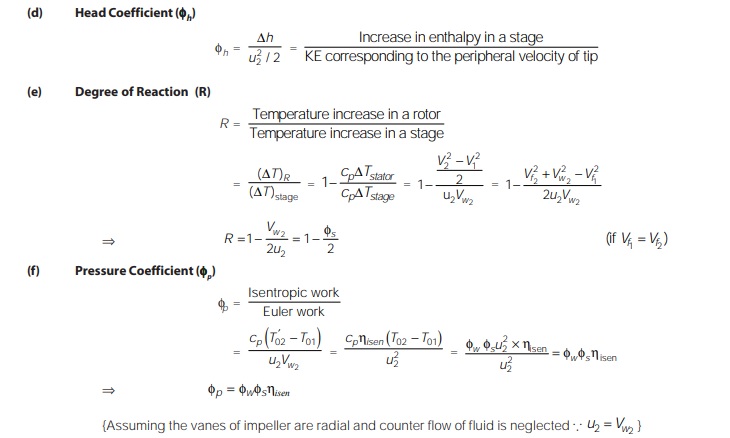
Dimensionless Parameter of Centrifugal Compressor
The energy transfer occurring in the impeller corresponding to real velocity profile is less than the one that would have been obtained with one dimensional flow, the apex of the actual velocity triangle at the impeller exit is shifted away (opposite to the direction of rotation) from the apex of the ideal velocity triangle. This phenomenon is known as slip and the shift of the apex is the slip velocity (Vs).
Slip = u2 –Vw2
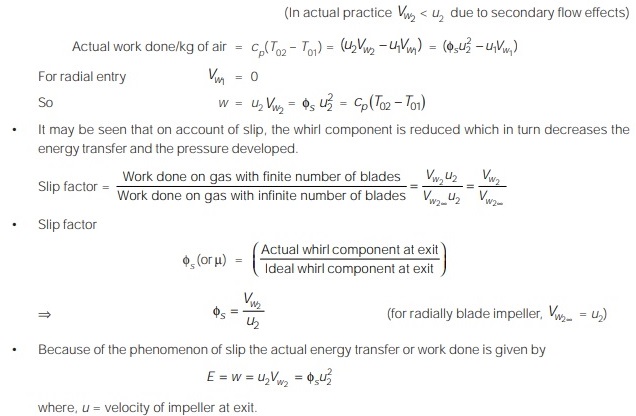

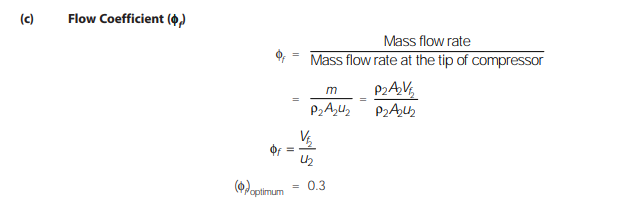
Losses in Centrifugal Compressor
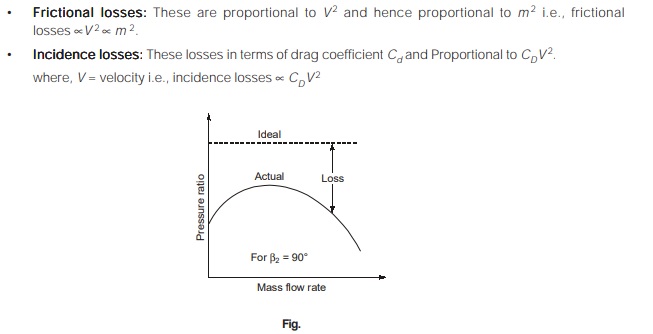
If the losses are subtracted from the ideal energy transfer for a radial vaned impeller, then the constant pressure ratio straight line characteristics becomes curved, with a maximum value of energy at some particular value of mass flow rate.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Power Plant Engineering?

