Types of Protection
There are mainly two types of protection:
Primary protection:
It is the first line of defence and ensures quick acting and selective clearing of faults within the boundary of the circuit section or element it protects. It is provided for each section of an electrical installation.
Back-up protection:
It is the second line of defence which function to isolate a faulty section of the system in case the main protection fails to function properly. Back-up protection is required because sometimes the associated CTs, PTs and circuit breakers of the protective scheme may fail to operate. It can be provided either on the same circuit breakers which would be normally opened by the main protection or by a second line of protection making use of different circuit breakers.
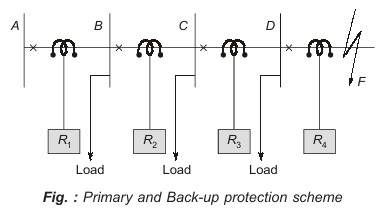
From the figure shown above, if a fault occurs at F then, the circuit breaker at D operates (for primary protection) and if anyhow circuit breaker D fails to operate then, the circuit breaker at C will operate (providing back-up protection) and will isolate the faulty section.
- Remote Back-up: When back-up relays are located at a neighbouring station, they back-up the entire primary protective scheme which includes the relay, circuit breaker, VT, CT and other elements, in case of a failure of the primary protective scheme.
- Relay Back-up: This is a kind of a local back-up in which an additional relay is provided for back up protection. It trips the same circuit breaker if the primary relay fails and this operation takes place without delay.
- Breaker Back-up: It is a kind of a local back-up. This type of a back-up is necessary for a bus bar system where a number of circuit breakers are connected to it.
Protective Relays
The relay in power system protection ensures the safety of the circuit equipment from any damage which might be otherwise caused by the fault.
All the relays have three main fundamental elements as shown below in figure.
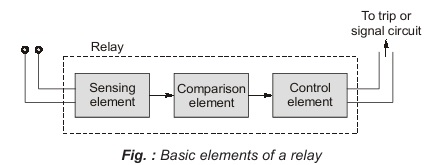
Sensing element: It is also called measuring element which responds to the change in the actuating quality. For example, current in a protected system in case of over current relay.
Comparing element: It compares the actuating quantity (i.e., current) with a pre-determined relay setting.
Control element: On pick-up of the relay, control element accomplishes a sudden change in the control quantity such as closing of the protective current circuit.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Power Generation?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

