Mesh Analysis with Current Sources
Applying mesh analysis to circuits containing current sources (dependent or independent) may appear complicated. But it is actually much easier than what we encountered in the previous section, because the presence of the current sources reduces the number of equations. Consider the following two possible cases.
CASE-1: When a current source exists only in one mesh: Consider the circuit shown below in figure, for example. We set i2 = –5 A and write a mesh equation for the other mesh in the usual way.
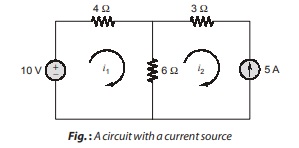
CASE-2: When a current source exists between two meshes: If a current source (Independent or dependent) is common between two meshes, we can create a supermesh by avoiding the current source and any elements connected in series with it. We thus reduce the number of meshes by 1 for each current source present. Kirchhoff’s voltage law is thus applied only to those meshes or supermeshes in the reinterpreted network.
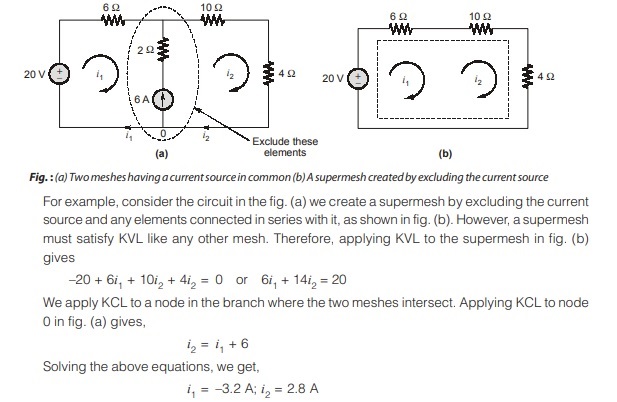
Steps to Determine Mesh Currents using Supermesh Analysis
- Step-1 : Determine if the circuit is a planar circuit. If not, perform nodal analysis instead.
- Step-2 : Count the number of meshes (M). Redraw the circuit if necessary.
- Step-3 : Label each of the M mesh currents. Generally, defining all mesh currents to flow clockwise results in a simpler analysis.
- Step-4 : If the circuit contains current sources shared by two meshes, form a supermesh to enclose both meshes. A highlighted enclosure helps when writing KVL equations.
- Step-5 : Write a KVL equation around each mesh/supermesh. Begin with a convenient node and proceed in the direction of the mesh current. Pay close attention to “–” signs. If a current source lies on the periphery of a mesh, no KVL equation is needed and the mesh current is determined by inspection.
- Step-6 : Express any additional unknowns such as voltages or currents other than mesh current in terms of appropriate mesh currents. This situation can occur if current sources or dependent sources appear in our circuit.
• Step-7 : Organize the equations. Group terms according to mesh currents. - Step-8 : Solve the system of equations for the mesh currents (there will be M of them).
Note:
- The current source in the supermesh provides the constraint equation necessary to solve for the mesh currents.
- A supermesh has no current of its own.
- A supermesh requires the application of both KVL and KCL.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Network Theory?

