Circuit Elements
Classification of Circuit Elements
An element is the basic building block of a circuit. By definition, a simple circuit element is the mathematical model of a two-terminal electrical device, and it can be completely characterized by its voltage-current relationship; it cannot be subdivided into other two-terminal devices.
For example,
- If the voltage across the element is linearly proportional to the current through it, then the element is called a resistor.
- If the terminal voltage is proportional to the derivative of current with respect to time, then the element is called an inductor.
- If the terminal voltage is proportional to the integral of current with respect to time, then the element is called a capacitor.
- If the terminal voltage is completely independent of current, or the current is completely independent of voltage, then the element is called an independent source.
- The element for which either the voltage or current depends upon a current or voltage elsewhere in the circuit; such elements are called dependent sources.
Classification of Network Elements
Active and Passive Elements
- Those devices or components that produce energy in the form of voltage or current are called active components. E.g., diodes, transistors.
- Active components are also called as energy donors. They do not require an external and conditional source to operate in the circuit. They have gained more than 1. So, they can amplify the signal. These circuit components can control the flow of current through the circuit.
- Those devices or components which store or maintain energy in the form of voltage or current are known as passive components. E.g., resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc. Passive components are also called as energy acceptors. Passive components require an external and conditional source to operate in the circuit. These components are incapable of providing any gain in energy and current.
Remember:
- The transistors provide power gain, so they are active elements, but transformers have the same power at input and output; they are not active elements.
- The active element should be able to provide power/power gain to the circuit for an infinite duration of time; that is why the charged capacitor or inductor is not an active element.
Bilateral and Unilateral Elements
- For a bilateral element, the voltage-current relationship is the same for current flowing in either direction. Resistors, inductors, and capacitors are examples of bilateral elements.
- For a unilateral element, the voltage-current relationship is different for two directions of current flow. A diode is a unilateral element.
Lumped and Distributed Elements
- Lumped elements are considered as the separate elements that are very small in size. For example, resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
- Distributed elements are not electrically separable. These are distributed over the entire length of the circuit. For example, transmission lines.
NOTE:
The size of a lumped element is small with respect to signal wavelength. At steady state we can consider a distributed element as a lumped element.
Linear and Non-linear Elements
- Linear Elements : These are elements in which the constituent relation, the relation between voltage and current is a linear function. They obey the homogeneity and additivity property. E.g., resistances, capacitances, inductances, and linearly dependent sources. The main function of a linear element is to oppose the current flow or energy storage or energy conversion.
- Non-Linear Elements : These are elements in which the relation between voltage and current is non linear function. These elements do not follow the additivity and homogeneity properties. E.g., diodes, transistors.
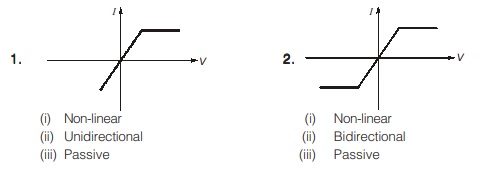
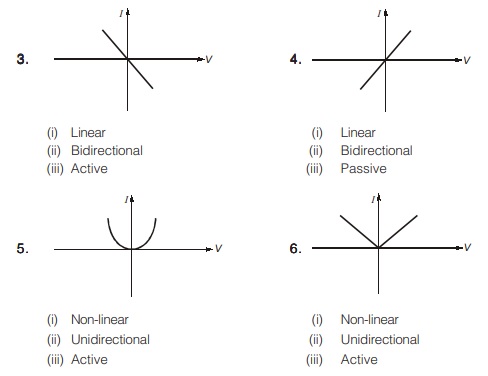
I-V Characteristic Curves for Different Elements
Following are given some I-V characteristic curves for different elements; looking at these characteristics, we can find the type of element.
Remember:
- If the characteristic curve is similar in opposite quadrants, then the element is bidirectional; otherwise, it is unidirectional.
- If the ratio of voltage to current at any point on the characteristic curve is negative, then the element is active; otherwise, it is passive.
- Every linear element must exhibit bidirectional property.
Characteristics
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Network Theory?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.