Comparison of lead and lag compensators
| Phase Lead Compensator | Phase Lag Compensator |
|---|---|
|
|
- Proportional (P) Controller
- Integral (I ) Controller
- Derivative (D) Controller
- Proportional Integral (P–I ) Controller
- Proportional Derivative (P–D) Controller
- Proportional Integral Derivative (P-I-D) Controller
Proportional (P) Controller
In proportional controller, the actuating signal for the control action in a control system is proportional to the error signal (which is the input to the controller), therefore the system is called proportional control system.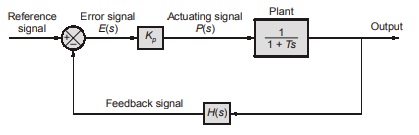
Integral (I) Controller (Reset Mode)
In integral controller, the actuating signal for the control action in a control system is proportional to the integral (or integration) of the error signal (which is the input to this controller), therefore the system is called integral control system.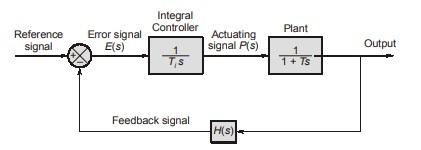
Derivative (D) Controller (Rate Mode)
In derivative controller, the actuating signal for the control action in a control system is proportional to the
derivative (or differentiation) of the error signal (which is the input to the controller), therefore the system is called
derivative control system.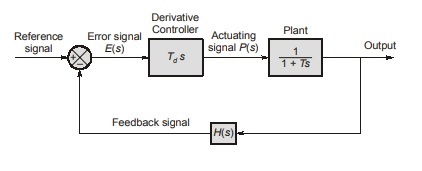
Proportional Integral (P-I) Controller
It is composite of proportional and integral controllers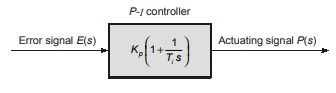
Proportional Derivative (P-D) Controller
It is composite of proportional and derivative controllers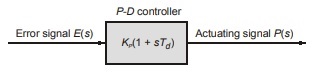
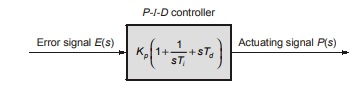
Proportional Integral Derivative (P-I-D) Controller
It is composite of proportional, integral and derivative controllers.
State variables analysis
State model of Linear systems:
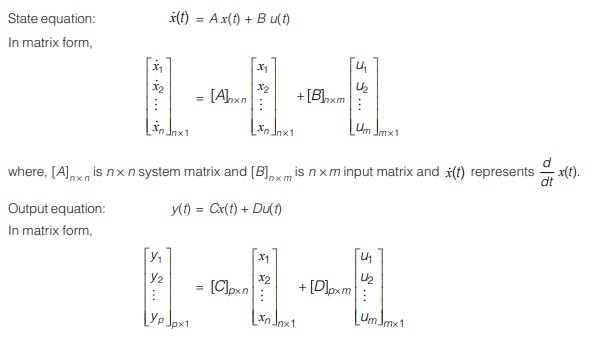
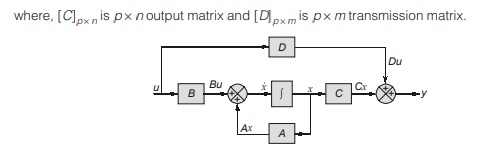
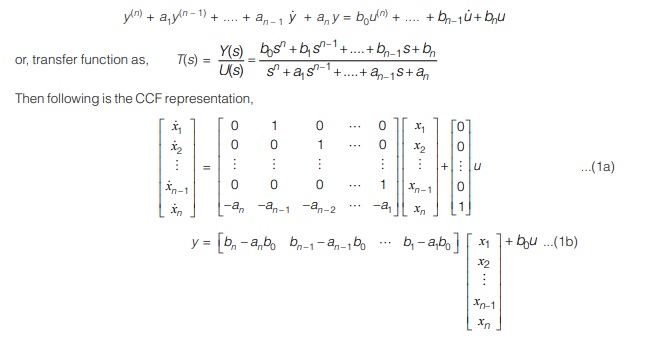
1. Controllable Canonical Form (CCF)
This form of state-space representation has got the name due to the fact that all of the states are feedback to the input.
Consider the linear system defined by,
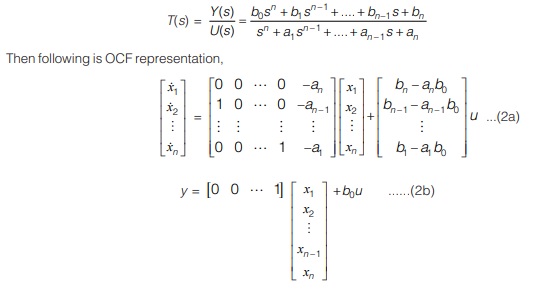
2. Observable Canonical Form (OCF)
In this form the feedback is from the output to the state variables and thus named as observable canonical or observer canonical form.
Consider the transfer function system,
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is a Control System?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

