What do you mean by Machine Instructions?
A set of binary codes that are recognised and executed directly by a processor is called a machine code. An individual machine code is called a machine instruction.
Main memory holds machine instructions and data.
Fields of an Instruction:
- Opcode: The operation itself is usually represented by a code called the opcode.
- Address: Other than opcode, all the other parts of an instruction are called address or operand fields.
- Mode: It specifies the way the operand or effective address is determined. It may be implicit or explicit in the instruction.
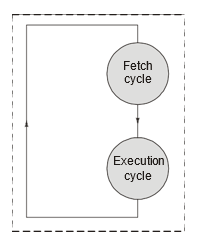
Instruction Cycle
Instruction cycle describes the execution sequence of the program instruction contain two sub cycles:
- Fetch cycle
- Execution cycle
Fetch Cycle
- Objective of a fetch cycle is instruction fetch. In this process, CPU fetch the instruction from main memory based on program counter.
Execution Cycle
- Objective of a execution cycle is processing of an instruction.
- CPU organisation is classified in the three types based on the availability of “ALU operands”:
- Stack CPU
- Accumulator CPU
- General register CPU
# Stack CPU
- In this organization ALU operations are performed only on stack data means both of the operands are always required into stack.
# Accumulator CPU
- In this organisation, for ALU operation Ist operand is always required in the accumulator while 2nd operand may be present either in the register or in the memory.
# General register CPU
- Based on the number of registers possible in the CPU, architecture is divided into two categories:
# Register to memory reference CPU.
# Register to register reference CPU.
#Register to memory reference CPU:
-
- In this architecture, number of registers are less in comparison with register to register reference CPU.
- In this architecture, for performing ALU operation it is needed to store first operand in the register while second operand can either be in register/memory.
- After processing, result is stored in the source 1 register.
- Compatible instruction format: “2 address instruction”

<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Computer Organization and Architecture?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

