LAW OF ACCIDENTAL ERROR
Theory of probability is used to study the behaviour of accidental errors. Error when plotted against the probability of its occurrence, we get normal probability distribution curve.
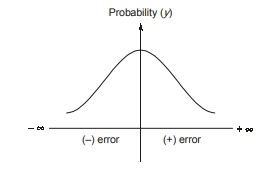
- Error = Measured value – true value.
- But as the true value of a measured quantity is never known, therefore true error will also be not known.
- Therefore in theory of probability, a value known as most probable value is commonly used. It is the value which is more close to the true value than any other value. It has more chances of being true.
- The difference between the measured value and most probable value is known residual error (variation).
- The frequency of residual error is depicted from probability distribution curve.
- The positive and negative errors are equal in size and frequency, as the curve is symmetrical.
- The small errors are more frequent than larger errors.
- A very large errors seldom occurs.
Gaussian Distribution
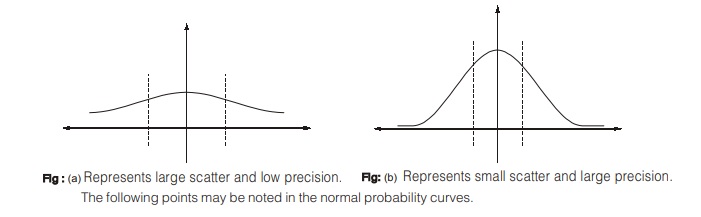
- The normal or Gaussian distribution is the most important of all types of distribution. It is also known as the bell-shaped distribution.
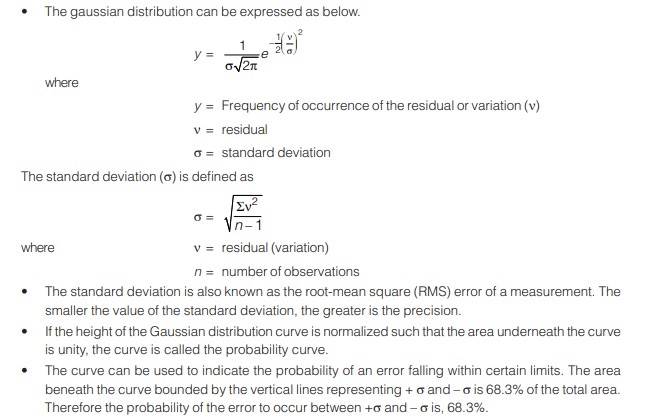
Standard Deviation
It is a numerical value that indicates the amount of precision about a central value.


Maximum Error
- The maximum error of a quantity is almost impossible to determine absolutely as the probability distribution curve extends to infinity. Thus, often 99.9% error is taken as the maximum error in This maximum error corresponds to ± 3.29s
- The maximum error is many a times used to separate mistakes from the random errors.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Surveying?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

