Defects in Rails
Corrugation in Rail (Roaring Rails)
- The minute depression on the rail surface due to application of break or during the start or due to abnormal load is known as corrugation.
- It induces high roaring sounds.
- The corrugated rails should be replaced as soon as possible because minute depressions are spreading in nature.
Hogged Rails
- Due to battering action of wheels over the end of the rails, the rails bent down and get deflected at the ends.
- This hogging at ends is due to loose packing under the joints and/or loose fish plate.
Remedial Measures
- Hogged ends are cut-off and fresh holes for fixing fish plates are provided — cropping. Hogged rails are entirely replaced.
- Deflected ends are brought to level by welding
Buckling of Rails
- It means track has gone out of its original alignment.
- It happens when expansion of rails due to temperature variations is prevented due to insufficient gap at joint so the rails do not get enough space for expansion. This results in widening of the gauges.
Remedial Measures
- Ballast, sleeper and rail sections must be checked for design.
- Providing steel sleeper
- Provision of expansion gap
- Not very strong tightening of fish bolts.
Kinking in Rails
- Due to loose packing of ballast and loose joint, the misalignment of the rail can take place at the joint known as kinking of rail. (In the joint portion)
Theory of Creep
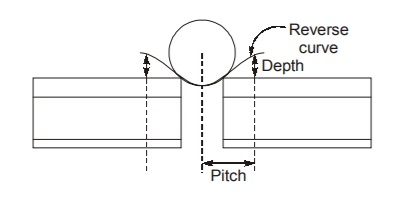 (a) Wave Theory
(a) Wave Theory
- As per wave theory, when wheel moves on track it forms a reverse curve and wheel actually pushes the reverse curve which results into forward movement of rail/creep.
- The depth of wave depends on stiffness of rail section, stability of foundation and track modulus.
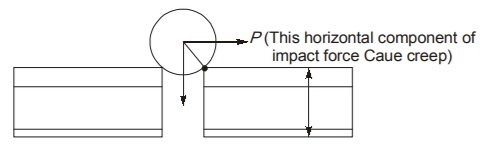
(b) Percussion Theory
- As per percussion theory, the longitudinal movement of rail occurs due to the impact force exert by wheel on the joint of the rail.
 (c)Drag Theory
(c)Drag Theory
- As per drag theory, when locomotive start moving it create a backward thrust to move forward.
- Due to the inertia effect, the wagons put forward thrust on the same rails.
- Now whichever thrust is higher creep will occurs in that direction (generally forward thrust is higher).
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Railway Engineering?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.