Traffic Rotaries
Rotary intersections are special form of intersection at grade laid out for the movement of traffic in one direction (clockwise) around a central traffic island. The vehicles entering the rotary are gently forced to move in a clockwise direction in orderly fashion. Then, they weave out of the rotary to the desired direction.
General Guidelines for the selection of rotaries
- Rotaries are suitable when the traffic entering from all the four approaches are relatively equal.
- A total volume of about 3000 vehicles per hour can be considered as the upper limiting case and a volume of 500 vehicles per hour is the lower limit.
- A rotary is very beneficial when the proportion of the right turn traffic is very high, typically if it is more than 30 percent.
- Rotaries are suitable when there are more than four approaches or if there is no separate lanes available for right turn traffic. Rotaries are ideally suited if the intersection geometry is complex.
Advantages of Rotary
- Traffic flow is regulated to only one direction of movement, thus eliminating severe conflicts between crossing movements.
- All the vehicles entering the rotary are gently forced to reduce the speed and continue to move at slower speed. Thus, none of the vehicles need to be stopped, unlike in a signalized intersection.
- Because of lower speed of negotiation about rotaries and elimination of severe conflicts, accidents and their severity are much less in rotaries.
- Rotaries are self governing and do not need practically any control by police or traffic signals.
- They are ideally suited for moderate traffic, especially with irregular geometry, or intersections with more then three or four approaches.
Disadvantages of Rotary:
- All the vehicles are forced to slow down and negotiate the intersection. Therefore, the cumulative delay will be much higher than channelized intersection.
- Even when there is relatively low traffic, the vehicles are forced to reduce their speed.
- Rotaries require large area of relatively flat land making them costly at urban areas.
- The vehicles do not usually stop at a rotary. They accelerate and exit rotary at relatively high speed.
Therefore, they are not suitable when there a is high pedestrian movements.
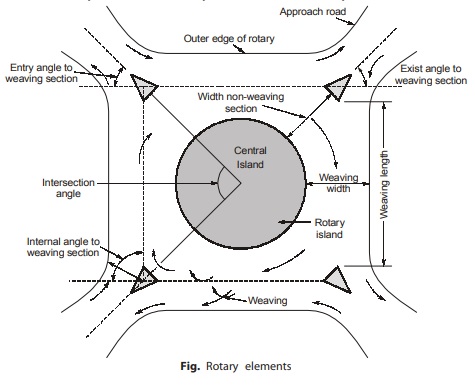
Capacity of the Rotary
Capacity of a rotary is determined by the capacity of each weaving section. Capacity of individual weaving sections depends upon
(i) Width of weaving section (w)
(ii) Average width of entry into rotary (e)
(iii) Weaving length (l)
(iv) Proportioning ratio (p)
Practical capacity of rotary in PCU per hour is given by

<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Highway Engineering?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.


