Model Analysis
- For predicting the performance of hydraulic structures (such as dam, spillway etc.) or hydraulic machines (such as turbines, pumps etc.), before construction or manufacturing, model of structure or machines are made and tests are performed on them to obtain desired information about how the structure or the machine would behave when it is actually constructed.
- The actual structure or machine is called ‘prototype’ prototype and the small (or sometimes large) scale replica is known as ‘model’
- The model tests are quite economical and convenient, because the design, construction and operation of the model may be altered several times if necessary (without incurring much expenditure), till all the defects of model are eliminated.
- Mostly the models are much smaller than the corresponding prototypes, but in some cases the models may be larger than the prototypes.
- There are two types of models that are usually constructed:
(i) Undistorted models (Geometrically Similar Model)
(ii) Distorted Model (In case of rivers, estuaries and harbour)
Theory of Distorted Models
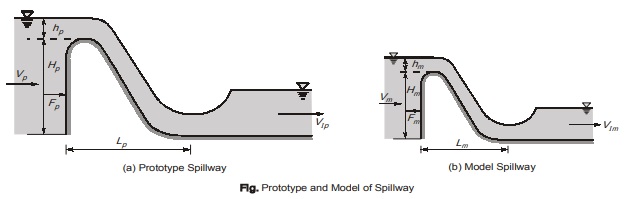
- An undistorted model is the one which is geometrically similar to its prototype i.e. the scale ratios for corresponding linear dimensions of the model and its prototype are same.
- But in some of the flow system like river flows, harbours, spillways the vertical dimensions are very less as compared to the horizontal dimension of the system. Therefore, different scale ratios are selected for the horizontal and vertical dimensions and such kind of models are known as distorted models. models
- Distorted models are not geometrically similar with their prototypes. Therefore, distorted models generally seen exaggerated on the vertical scale.
- A distorted model may have either geometrical distortion or material distortion, or distortion of hydraulic quantities.
- In geometrical distortion, distortion can be either of dimension or configuration.
- The material distortion takes place when physical properties of corresponding materials in model and in prototype do not satisfy similitude condition.
- Distorted models are required to be prepared for rivers, dams, harbours, estuaries etc.
Following are some of the reasons for adopting distorted models:
- To maintain accuracy in vertical measurement.
- To maintain turbulent flow.
- To obtain suitable bed material and its adequate movement.
- To obtain suitable roughness condition.
- To accommodate the available facilities such as space, water supply, money, and time.
River Model Law
- In such models, Froude law is the basic similitude criteria.
- The models may have either vertical exaggeration or slope exaggeration.
- In a model with vertical exaggeration, the depth scale is exaggerated.
- On the other hand in a model with slope exaggeration, the model is provided with relatively larger slope by tilting it.
- Let LrH and Lrv are the horizontal and vertical scale ratio. Thus,
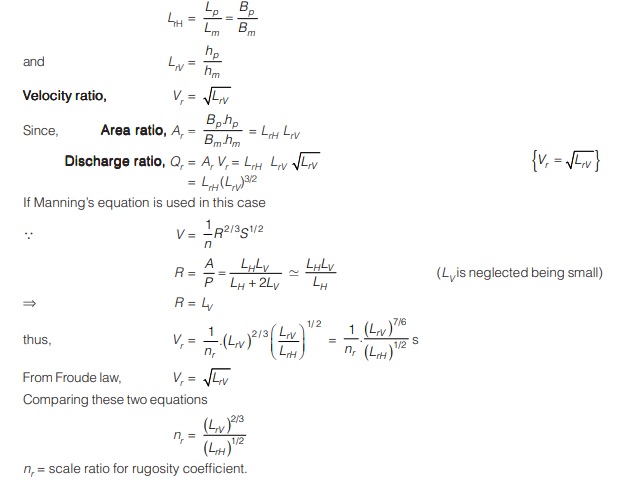
Drag
- The drag on the body is given by the summation of the components of the forces acting over the entire surface of the body in the direction of the fluid motion. The sum of the components of the shear force in the direction of flow is called friction drag friction drag and it is given by
![]()
- Similarly, the sum of the components of the pressure force in the direction of flow called pressure drag and can be expressed as
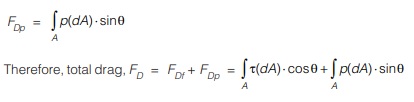
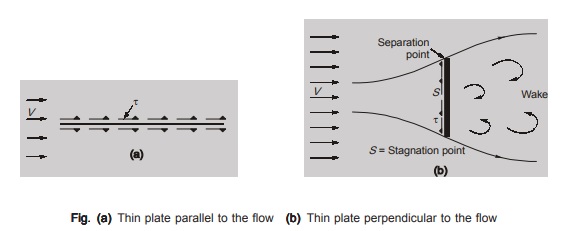
- The relative magnitude of the two components of the total drag viz., friction drag and pressure drag, depends on the shape and the position of the immersed body. Thus, if a thin flat plate is held immersed in a fluid, parallel to the direction of flow, the pressure drag is practically equal to zero. As such in this case the total drag is equal to the friction drag. The vice-versa is the case for plate placed perpendicular to the flow direction of flow.
Lift
- The lift on the body is given by the summation of the component of the shear and the pressure forces acting over the entire surface of the body in the direction perpendicular to the direction of the fluid motion. Thus, following expression is obtained for the total lift FL acting on the body. The total lift is the sum of lift due shear force and lift due to normal pressure.

<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Fluid Mechanics?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

