Sedimentation Tanks
Type of Sedimentation Tanks
There are two types of sedimentation tank:
(a) Quiescent type
(b) Continuous type
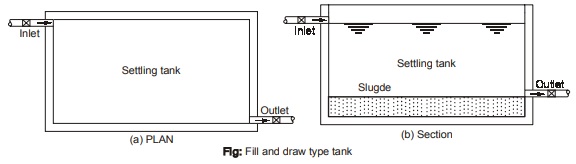
(a) Quiescent Type (Fill and Draw Type)
In this type, Tank is filled with incoming water and is allowed to rest for a certain time. During this time, suspended particles settle at bottom of tank. Generally, 24 hrs detention period is provided and 6 to 12 hrs required for sludge removal (i.e. cleaning the tank), therefore total cyclic operation need 30 to 36 Hrs. Hence, minimum three tanks are required to maintain constant supply.
(b) Continuous flow type tank
Velocity of flow is one parameter among the three (velocity of flow, viscosity of water, size and shape of particle) parameter that can be easily controlled. In quiescent type tank, water was stored in tank for certain period, while in a continuous flow type tank, water continuously keeps on moving in the tank, though with a very small velocity to reduce the turbulence of water in order to help the suspended particles in settling.
Basically, there are two types of tank:
(i) Horizontal flow tank
(ii) Vertical or upflow tanks
These tanks may be rectangular or square in plan.
(i) Horizontal flow tanks: While designing horizontal flow tanks, it is tried to achieve ideal conditions of equal velocity at all points lying on each vertical line in settling zone. Direction of flow in tank is substantially horizontal. There can be two types of tank for designing of horizontal flow type tank.
Rectangular tanks with longitudinal flow
In these type of tanks, water enters from one end and comes out from the other end. The tank is rectangular in plan and flow is in longitudinal direction in these type of tanks. A sufficient length of travel is provided to water so as to reduce its velocity to a considerable extent. Also, the velocity is reduced to that extent so that time taken by suspended particle to travel from one end to other is slightly more than time required for settlement of that particle. An example of rectangular tank is shown in figure below:
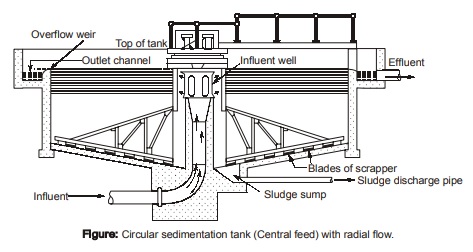
(b) Vertical or upflow settling tanks: They may be square or circular in plan, and may have hopper bottom. The influent enters at bottom of unit. The upflow velocity decreases with increased cross sectional area of tank. The effluent water is withdrawn through circumferential or circular weir.
Design data for plain sedimentation tank
Following design consideration should be taken into account while designing for plain sedimentation tanks.
- Overflow rate vary between 12-18 m3/day/m2 of plan area.
- Detention time is taken as 4 to 8 hrs.
- Width of tank is taken as 10 m and not allowed to exceed 12 m.
- Length/width ratio is generally taken as 4.
- Flow of velocity is generally taken as 0.3 m/min.
- It is designed for maximum daily demand.
- Values of overflow rate vary between 24-30 m3/day/m or plan area for sedimentation tanks using coagulants as aids.
- Detention time usually ranges from 2 to 4 hours in coagulation aided sedimentation tank.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Environmental Engineering?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

