Interference Among Wells
If two or more wells are constructed very close to each other such that their cones of depression intersect, they are said to interfere each other. Due to interference, yield of wells are decreased. Muskat has proposed the following formulae for computation of discharges from such interfering wells:
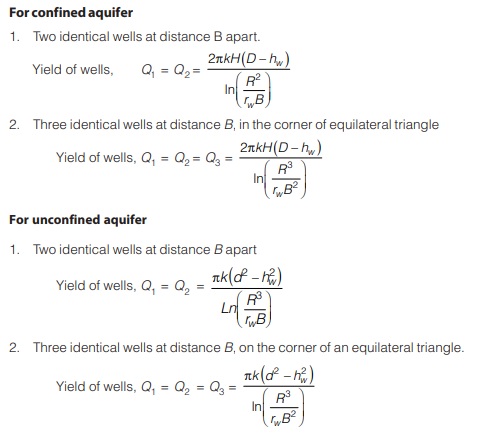
THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND WATER QUALITY
Water is one of the most abundant compounds found in nature, covering approximately three-fourths area of the earth. Inspite of this apparent abundance, several factors serve to limit the amount of water available for human use.
Over 97% of the total water supply is contained in the oceans and other saline bodies of water and is not readily usable for most purposes. Of the remaining 3%, a little over 2% is tied up in ice caps and glaciers and, along with atmospheric and soil moisture, is inaccessible. Thus, for general livelihood and the support of their varied technical and agricultural activities, humans must depend upon the remaining 0.62% water found on fresh water lakes, rivers and ground water supplies.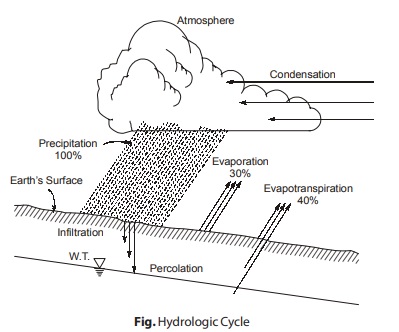
Water is in a constant state of motion depicted in the hydrologic cycle as shown in figure. Atmospheric water condenses and falls to the earth as rain, snow or some other term of precipitation. On the earth’s surface, water flow into streams like lakes and eventually the oceans or percolates through the soil and into aquifers than eventually the oceans, discharge into surface waters. Water in nature is most nearly pure in its evaporation state. The impurities accumulated by water throughout the hydrologic cycle and as a result of human activities may be in both suspended and dissolved form. Dissolved material consists of molecules or ions that are held by the molecular structure of water. Colloids are very small particles that technically are suspended. Size range of dissolved, colloidal and suspended substances are shown in figure.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
Dissolved solids in water come from inorganic salts such as CaCl2, Na2CO3, NaCl, MgSO4 etc. and organic metters such as hydrocarbons and sugars etc.
![]()
(a) Measurement
Measurement of total dissolved solid is done by following methods as:
(i) Gravimetric method
It is an exact method. In this method, firstly, a known volume of water sample is passed through filter (Whatman filter) having pore size 1.2 µm so that suspended solids being bigger in size remains on filter and dissolved solids remains in water sample. After that sample is heated at 103 – 105°C so that water is evaporated leaving behind the dissolved solids. Now, the residue is weighed in order to obtain the mass of total dissolved solids. Dissolved solids are expressed in mg/L.
(ii) Specific conductivity test
It is an approximate and quick method of determining total dissolved solids in a water sample. Analysis of TDS is measured by determining the electrical conductivity of water.
Mathematically,
(Electrical conductivity in µMho/cm at 25°) × 0.65 = Dissolved solids in mg/L
(b) Permissible limit
As per IS 10500: 2012, The acceptable limit of TDS is 500 mg/L and permissible limit in absence of other source is 2000 mg/L.
pH
pH value is the logarithm of reciprocal of hydrogen ion activity in moles per litre. It is thus an indicator of acidity or alkalinity of water. In water, molecules (H2O) are dissociated into two ions- the hydroxyl (OH–) ions or anions which are negatively charged and hydrogen. (H+) ions or cations which are positively charged. The concentration of
these two free or uncombined components is extremely small, but is governed by following law of mass action:

If an acid is added to pure water, hydrogen ion concentration in water will increase. Since, pH value is logarithm of reciprocal of hydrogen ions, therefore with increase in hydrogen ion concentration, pH value of water will decrease.
Hence, pH value of less than 7 indicates that water sample is acidic.
Similarly, if an alkali is added to pure water, hydroxyl ion concentration in water will increase. As the sum of concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions is to remain constant, therefore increase in hydroxyl ion concentration will decrease hydrogen ion concentration in water and consequently will increase the pH. Hence, if the sample of water has pH value of more than 7, then sample will be alkaline or basic in nature.
(a) Measurement
As per IS:3025 part-II, measured of pH is done by
(i) Electrometric method
In this method, pH value is determined by measurement of electromotive force of a cell consisting of an indicator electrode immersed in sample and a reference electrode (usually mercury/calomel electrode) contact between sample and reference electrode is usually achieved by means of a liquid junction, which forms part of reference electrode. The electromotive force is measured with a pH meter, which is a high impedance voltmeter calibrated in terms of pH.
(ii) Colorimetric method
In this method, a series of indicators and buffer solutions are used for determination of pH value by visual comparison universal.
Indicator is prepared by dissolving 0.05 g of methyl orange, 0.15 g of methyl red, 0.3 g of bromoethymol blue and 0.35 g of phenolphthalein, in one litre of alcohol. The colour changes are
| pH | Colour |
|---|---|
|
Upto3 |
Red |
|
4 |
Orange red |
|
5 |
Orange |
|
6 |
Yellow |
|
7 |
Yellowish green |
| 8 |
Greenish blue |
| 9 |
Blue |
| 10 |
Violet |
| 11 |
Reddish violet |
(b) Objection
1. If water is acidic, it will cause corrosion of pipe.
2. If water is alkaline, it will cause in crustation of pipe.
(c) Permissible limit
As per IS 10500:2012, acceptable limit of pH is 6.5 – 8.5 and permissible limit in the absence of alternate source is < 6.5 and > 9.2.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Environmental Engineering?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

