What is Probable Maximum Precipitation (PMP)?
- Probable maximum precipitation (PMP) is the maximum possible precipitation that can reasonably be expected at a given location.
- Probable maximum precipitation (PMP) is defined as the greatest or extreme rainfall for a given duration that is physically possible over a station or basin.
- PMP can be statistically estimated as
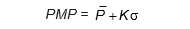

NOTE:
- A list of world’s greatest rainfall is made with the available data and plotted on log-log scale, the data seems to be in line and envelope of straight line can be used for other data also.
Pm = 42.16 D 0.475
where, Pm = extreme rainfall depth in cm, D = Duration in hours.
Depression Storage
When the precipitation reaches to the ground, firstly it must fill all the depression before it can flow over the surface. The volume of water trapped in these depression does not contribute to the runoff so these are called depression storage.
Depression storage depends on many factor, such as
(i) The type of soil (ii) Condition of surface
(iii) Nature of depression (iv) Slope of catchment
(v) Antecedent precipitation
From the experiment on different soil we are able to take some values for depression storage loss during intensive storms.
|
Sand |
0.5 cm |
|
Loam |
0.4 cm |
| Clay |
0.25 cm |
Measurement of Infiltration
Infiltration characteristics of a soil at a given location can be estimated by:
- Using flooding type infiltrometers
- Rainfall simulator
- Hydrograph analysis
- Flooding type infiltrometers: This is a simple instrument consisting of a metal cylinder, open at both ends. The cylinder is driven into the ground and water is poured into it from top. As the infiltration proceeds, water level goes down. To keep the water level at same initial point we add some water into it. As we know volume of water added, plot of infiltration capacity vs time is obtained. This experiment takes nearly 2-3 hours for completion.
- Rainfall Simulator: In this experiment, a small land of about 2 m × 7 m is provided with a series of nozzle on the longer side and arrangement is provided to collect and measure the surface runoff rate. The nozzles are specially designed to produce artificial rain of various intensities. By taking different combination of intensity and duration, surface runoff rate and volume are measured in each Using the water budget equation, the infiltration rate is also measured. If the artificial rainfall intensity is higher than the infiltration rate, we calculate the infiltration capacity also.
Rainfall simulator type infiltrometer give lower values than flooding type infiltrometer, because it takes the effect of rainfall impact. This test is not performed when heavy wind blows. - Hydrograph Analysis: Reasonable estimation of infiltration capacity of a small watershed can be obtained by analysing measured runoff hydrographs and corresponding rainfall records. If sufficiently good rainfall records and runoff hydrographs corresponding to isolated storms are available then water budget equation can be applied to estimate the abstraction by infiltration.
It gives good result for small watershed with fairly homogenous soil.
<< Previous | Next >>
Must Read: What is Hydrology in Civil Engineering?
Dear Aspirants,
Your preparation for GATE, ESE, PSUs, and AE/JE is now smarter than ever — thanks to the MADE EASY YouTube channel.
This is not just a channel, but a complete strategy for success, where you get toppers strategies, PYQ–GTQ discussions, current affairs updates, and important job-related information, all delivered by the country’s best teachers and industry experts.
If you also want to stay one step ahead in the race to success, subscribe to MADE EASY on YouTube and stay connected with us on social media.
MADE EASY — where preparation happens with confidence.

MADE EASY is a well-organized institute, complete in all aspects, and provides quality guidance for both written and personality tests. MADE EASY has produced top-ranked students in ESE, GATE, and various public sector exams. The publishing team regularly writes exam-related blogs based on conversations with the faculty, helping students prepare effectively for their exams.

